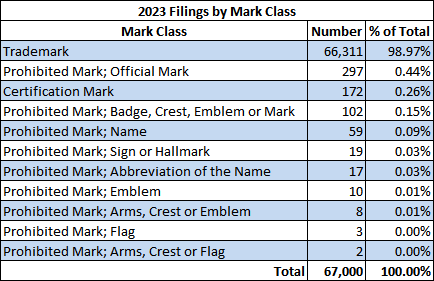
This post provides a mark type / class / category / status breakdown of the 67,000 trademark applications1 CIPO received in 2023.
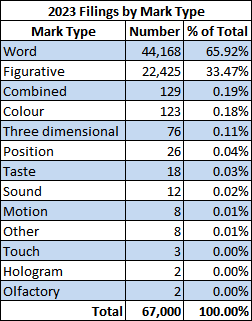
2023 filings break down by mark type as shown below. Most Canadian trademarks have only one mark type, but multiple types are possible2. This table reflects only the first mark type presented in CIPO’s data for each application.
1 This includes all types of applications handled by CIPO’s Trademarks Branch, e.g. trademarks, certification marks, official / prohibited (i.e. Section 9) marks, geographical indications, plant variety denominations, etc. Bear in mind that the filing date of an inbound Madrid Protocol application is deemed to be the international registration date of the corresponding Madrid registration; and that it can take weeks or months for a Madrid application to arrive at CIPO. Accordingly, a count of 2023 filings including Madrid filings may change depending on when the count is done.↩
2 For example registration TMA1106725 has 3 mark types: Design, Three-dimensional (3-D) and Mode of Packaging Goods. Some applicants appear to have difficulty selecting the appropriate mark type(s). For example as of 31-Dec-2023 application no. 2055585 asserts 10 mark types: Design, Motion, Hologram, Mode of Packaging Goods, Three-dimensional (3-D), Position, Taste, Sound, Scent, Texture. This will presumably require further consideration during prosecution.↩
3 See General vs. Specific Marks.↩
4 For an explanation of the Mark Protected by Federal Act of Incorporation class see Nurses!? What about Kinsmen / Canadian Clubs?↩
5 See Standardization Marks.↩
6 See Union Labels.↩
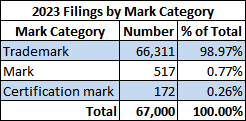
7 In CIPO’s parlance, the “trademark” category includes certification marks (even though there is a separate certification mark category), distinguishing guises, specific marks, standardization marks and union labels; whereas the “mark” category includes Plant Breeders Rights denominations, geographical indications, official / prohibited (i.e. Section 9) marks, etc.↩